Anecdotal reports from patients using cannabidiol (CBD) on top of their standard medication suggests that CBD might decrease inflammation, pain and comorbidities related to RA.
Summary Points:
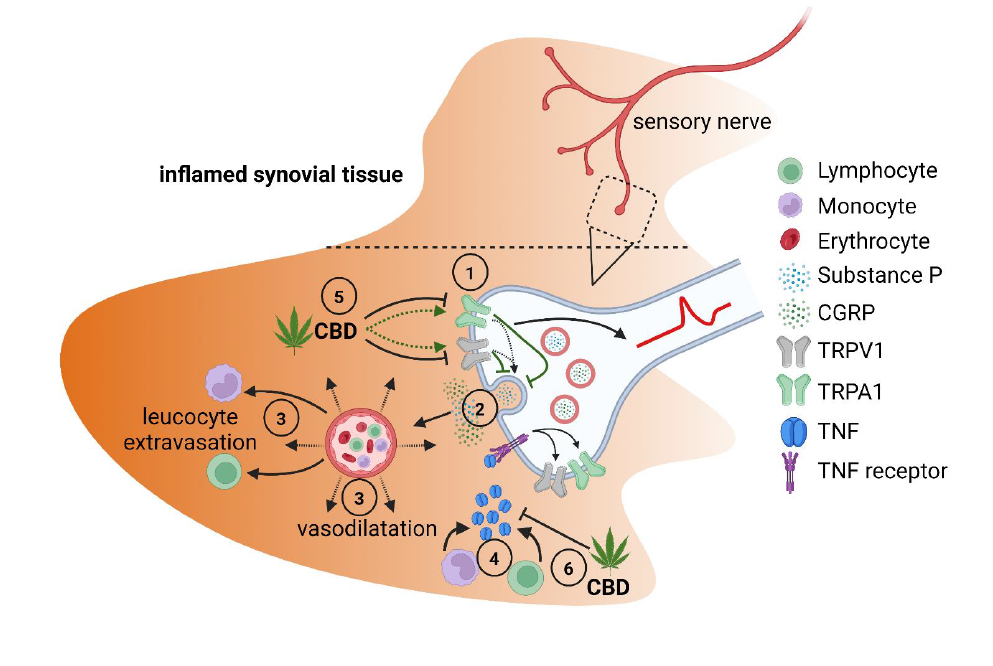
- CBD inhibits optimally activated T cells and reduces IL-2 and IFN-γ production while promoting T reg development in suboptimally activated T cells
- CBD reduces CCL-3, CCL-4, IL-6, IL-8, TNF and IL-10 production by B cells
- CBD enhances drug uptake by B cells and synovial fibroblasts
- CBD enhances or reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine production by macrophages depended on activation stimulus
- CBD induces cell death in monocytes and synovial fibroblasts
- CBD ameliorates experimental arthritis in mice
- Effects of CBD on arthritic pain are unclear
- CBD might curb RA-associated comorbidities such as hypertension and depression
- If liver toxicity can be excluded, CBD might be added to a given RA treatment regimen
- Besides limiting inflammation, CBD might enhance the efficacy of small molecule RA therapeutics
Source: Lowin T. Chapter 42 – Cannabidiol (CBD) and potential in medicinal use in rheumatoid arthritis. Medicinal Usage if Cannabis and Cannabinoids. 2023; 511-521